How to Pass Numerical Reasoning (20 page)
Read How to Pass Numerical Reasoning Online
Authors: Heidi Smith

Adding decimals: practice drill
Q1 | 74.8 |
Q2 | 249.75 |
Q3 | 87.043 |
Q4 | 186.91 |
Q5 | 0.003 |
Q6 | 15.6202 |
Q7 | 2.563 |
Q8 | 0 |
Q9 | 9.2 |
Q10 | –123.26 |
Subtracting decimals: practice drill
Q1 | 1.05 |
Q2 | 1.19 |
Q3 | 6.962 |
Q4 | 1.01 |
Q5 | 0.001 |
Q6 | 3.4 |
Q7 | 2.5583 |
Q8 | –9.9171 |
Q9 | 12.8078 |
Q10 | –0.009 |
Multiplying decimals: practice drill
Q1 | 23.04 |
Q2 | 134.2 |
Q3 | 6.92 |
Q4 | 21 |
Q5 | 1.44 |
Q6 | 111.55 |
Q7 | 1.22221 |
Q8 | 3.0804 |
Q9 | 0.1014 |
Q10 | 0.000003 |
Dividing decimals: practice drill
Q1 | 12 |
Q2 | 20 |
Q3 | 25 |
Q4 | 23 |
Q5 | 17 |
Q6 | 21 |
Q7 | 8.25 |
Q8 | 0.2 |
Q9 | 6.2 |
Q10 | 2.3 |
• Terms used in this chapter
• Converting units
• Working with rates
• Work rate problems
• Answers to
Chapter 3
Rate:
A ratio that establishes the relationship between two or more different quantities measured in different units.
Knowledge of rates is very useful for any commercial activity that requires you to measure productivity. A key measure of industrial performance may be the rate at which a finished part is produced, for example the number of surfboards waxed in a day or the number of barrels of oil extracted per month. Worker productivity may be measured by the completed number of manual tasks, such as the number of birthday cakes iced per hour or the number of violins varnished in a week. While these formulae do not account for quality control, you may apply an additional formula to find out, for example, the number of birthday cakes spoilt per week during the icing process.
Before we reintroduce the formulae to work out rates questions, a word or two on units. Rates are a useful method to compare different units, but like units must be measured in comparable terms. For example, you cannot always make a useful comparison between ‘miles per gallon’ and ‘kilometres per gallon’ or between ‘parts produced per worker’ and ‘parts produced per production line’. The following drills aim to hone your quick conversion skills and will remind you of the common units that you are likely to come across in your test. Where it is critical to know conversion rates, the test will typically contain this information. However, sound knowledge of these common equivalents will help you to calculate your answers quickly and save you those valuable seconds.
Time
Time is the unit that is most frequently converted when working with rates. The basic units of time are seconds, minutes and hours, and you will be required to convert units of time easily between the other time units. The following table is a guide to common time units.
Fraction of hour | Number of minutes |
1 | 6 minutes |
2 | 12 minutes |
3 | 18 minutes |
4 | 24 minutes |
5 | 30 minutes |
6 | 36 minutes |
7 | 42 minutes |
8 | 48 minutes |
9 | 54 minutes |
1 | 20 minutes |
2 | 40 minutes |
1 | 10 minutes |
5 | 50 minutes |
1 | 15 minutes |
3 | 45 minutes |
Distance
Distance is another unit that you may be required to convert. The table below gives the common equivalents of metric measures of distance. You will have the opportunity to practise these conversions in the practice drills.
To convert | Equivalents | Calculation |
Km to metres | 1 km = 1,000 m | Multiply the number of kilometres by 1,000 |
Km to cm | 1 km = 100,000 cm | Multiply the number of kilometres by 100,000 |
Km to mm | 1 km = 1,000,000 mm | Multiply the number of kilometres by 1,000,000 |
Metres to km | 1 m = 0.001 km | Divide the number of metres by 1,000 |
Metres to cm | 1 m = 100 cm | Multiply the number of metres by 100 |
Metres to mm | 1 m = 1,000 mm | Multiply the number of metres by 1,000 |
Cm to km | 1 cm = 0.00001 km | Divide the number of cm by 100,000 |
Cm to metres | 1 cm = 0.01 m | Divide the number of cm by 100 |
Cm to mm | 1 cm = 10 mm | Multiply the number of cm by 10 |
Mm to km | 1 mm = 0.000001 km | Divide the number of mm by 1,000,000 |
Mm to metres | 1 mm = 0.001 m | Divide the number of mm by 1,000 |
Mm to cm | 1 mm = 0.1 cm | Divide the number of mm by 10 |
Common units
To convert… | Equivalents | Calculation |
Years to weeks | 1 year = 52 weeks | Multiply the number of years by 52 |
Weeks to days | 1 week = 7 days | Multiply the number of weeks by 7 |
Weeks to hours | 1 week = 168 hours | Multiply the number of weeks by 168 |
Weeks to minutes | 1 week = 10,080 minutes | Multiply the number of weeks by 10,080 |
Days to hours | 1 day = 24 hours | Multiply the number of days by 24 |
Hours to minutes | 1 hour = 60 minutes | Multiply the number of hours by 60 |
Hours to seconds | 1 hour = 3,600 seconds | Multiply the number of hours by 3,600 |
Minutes to seconds | 1 minute = 60 seconds | Multiply the number of minutes by 60 |
Feet to inches | 1 foot = 12 inches | Multiply the number of feet by 12 |
Miles to km | 1 mile = approx. 1.61 km | Multiply the number of miles by 1.61 |
Km to miles | 1 km = approx. 0.62 mile | Multiply the number of km by 0.62 |
Ounces to grammes | 1 oz = 25 grammes | Multiply the number of ounces by 25 |
Inches to cm | 1 inch = 2.5 cm | Multiply the number of inches by 2.5 |
Pints to millilitres | 1 pint = 570 ml | Multiply the number of pints by 570 |
Farenheit to Celcius | (F – 32) × 0.55 | Subtract 32 from the number of degrees F and multiply by 0.55 |
Celcius to Farenheit | (C × 1.8) + 32 | Multiply the number of degrees C by 1.8 and add 32 |
Rates conversion practice: drill 1: time
Set a stopwatch and aim to complete the following drill in three minutes.
Q1 |
| = | minutes |
Q2 |
| = | minutes |
Q3 |
| = | minutes |
Q4 |
| = | minutes |
Q5 |
| = | minutes |
Q6 | 480 minutes | = | hours |
Q7 | 320 minutes | = | hours |
Q8 | 280 minutes | = | hours |
Q9 | 50 minutes | = | hour |
Q10 | 144 minutes | = | hours |
Q11 | 37 minutes | = | seconds |
Q12 | 36 seconds | = | hour |
Q13 |
| = | seconds |
Q14 |
| = | seconds |
Q15 | 48 minutes | = | hour |
Q16 |
| = | seconds |
Q17 |
| = | seconds |
Q18 | 20 seconds | = | minute |
Q19 |
| = | minutes |
Q20 | 0.2 hour | = | minutes |
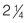 hours
hours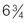 hours
hours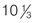 hours
hours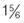 hours
hours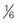 hour
hour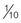 hour
hour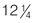 hours
hours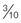 hour
hour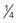 hour
hour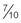 hour
hour