Pediatric Primary Care Case Studies (39 page)
Read Pediatric Primary Care Case Studies Online
Authors: Catherine E. Burns,Beth Richardson,Cpnp Rn Dns Beth Richardson,Margaret Brady
Tags: #Medical, #Health Care Delivery, #Nursing, #Pediatric & Neonatal, #Pediatrics

The female is 2 to 10 times more likely to experience a noncontact sports anterior cruciate ligament injury than a male. These injuries commonly occur during deceleration, landing, or cutting activities (Griffin et al., 2003).
The anatomy and biomechanics of the patellofemoral joint also put the female athlete at greater risk of having a problem with this joint. Malalignment or an imbalance between muscles of the pelvis, hip, knee, ankle, and foot; articular cartilage lesions; instability; soft tissue factors; and psychosocial factors can contribute to pain and dysfunction of this joint. Additionally, improper training, overuse, or injury can contribute to the pathophysiology. Runners can be afflicted with a painful knee condition known as
runner’s knee;
it results from overuse and causes micro-trauma to the sleeve of the knee joint.
Distinguishing factors include pain
around
the knee joint (rather than
inside
it) and initial minor discomfort that progresses to increased pain after running.
The Use of Medroxyprogesterone (Depo-Provera) by the Female Athlete
Since 2004, the Food and Drug Administration has required a “black box” warning about the use of medroxyprogesterone as a contraceptive for adolescents and young adults. Some studies had found that prolonged use resulted in loss of bone mineral density; the loss was duration dependent. Current prescribing recommendations, therefore, advise not using this method of contraception in this age group for longer than 2 years
unless
there is no other alternative (American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, 2008).
What parts of the physical examination do you want to emphasize?
Physical Examination
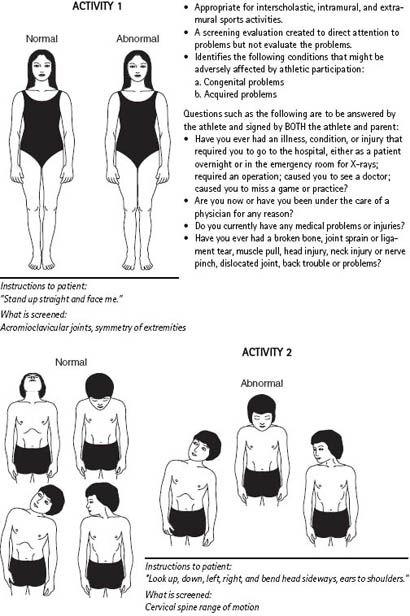
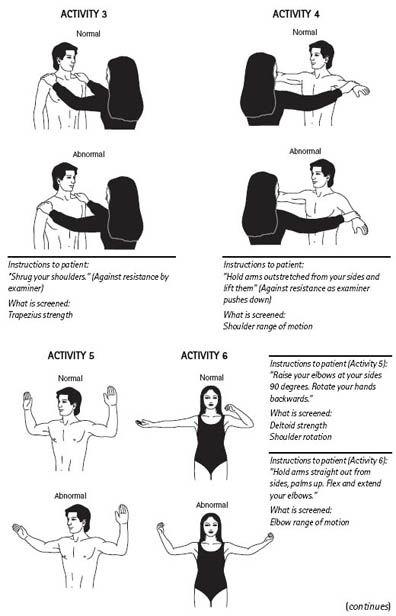
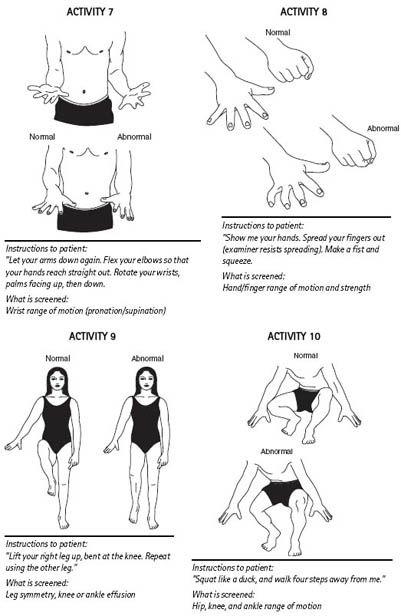
The PPE should consist of two parts, the musculoskeletal and general physical examinations. The simple, standardized 90-second musculoskeletal screening (
Figure 10-2
) reliably detects 90% of significant injuries, and has a 51% sensitivity and 97% specificity (McCarthy, 2006). Limitations or dysfunction in alignment, flexibility, and proprioception will be detected.
Table 10-2
shows the components of an appropriate general organ examination. You want to pay special attention to assessing Nikola’s mental status because of her prior head injury, her musculoskeletal examination because of her prior stress fracture history, and her growth parameters and pulse because of concerns regarding her nutrition and eating habits.
Nikola’s examination reveals the following:
Height: 67 inches (slightly under 90%)
Weight: 127 pounds (approximately 60%)
BMI: 20 (between 25% and 50%)
Blood pressure: 115/68, Pulse: 60
Snellen: 20/20 OD/OS/OU with glasses
Appearance: Alert, cooperative, good historian, good eye-to-eye contact, smiles frequently, slender
The examination is negative except for a Grade I/VI, short, musical, midsystolic murmur best heard at the apex without radiation, increased slightly when supine.
What diagnostic studies would you consider?
The only routine diagnostic test for a PPE is a hemoglobin/hematocrit for females, unless there is a particular risk factor for the individual. Females are more at risk for iron deficiency anemia. Urine drug screening and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) testing may be required by some organizations.