How to Pass Numerical Reasoning (3 page)
Read How to Pass Numerical Reasoning Online
Authors: Heidi Smith

Dividing and multiplying numbers
Long multiplication
Rapid multiplication of multiple numbers is easy if you know the multiplication tables inside-out and back-to-front. In a long multiplication calculation, you break the problem down into a number of simple calculations by dividing the multiplier up into units of tens, hundreds, thousands and so on. In
Chapter 2
you will work through practice drills involving division and multiplication of decimals.
Worked example
Q. What is the result of 2,348 × 237?
To multiply a number by 237, break the problem down into a number of simpler calculations. Divide the multiplier up into units of hundreds, tens and units.
For example, to multiply by 237 you multiply by:
7 (units)
3 (tens)
2 (hundreds)
(It doesn’t matter in which order you complete the calculation.)

Long multiplication: practice drill 1
No calculators! This exercise is intended to help you to speed up your mental arithmetic. Set a stopwatch and aim to complete this drill in five minutes.
Q1 | 12 | × | 24 |
Q2 | 13 | × | 23 |
Q3 | 11 | × | 23 |
Q4 | 19 | × | 19 |
Q5 | 26 | × | 24 |
Q6 | 213 | × | 43 |
Q7 | 342 | × | 45 |
Q8 | 438 | × | 23 |
Q9 | 539 | × | 125 |
Q10 | 5,478 | × | 762 |
Long multiplication: practice drill 2
Set a stopwatch and aim to complete this practice drill in five minutes.
Q1 | 9 | × | 18 |
Q2 | 11 | × | 19 |
Q3 | 12 | × | 21 |
Q4 | 19 | × | 23 |
Q5 | 26 | × | 19 |
Q6 | 211 | × | 17 |
Q7 | 317 | × | 13 |
Q8 | 416 | × | 11 |
Q9 | 624 | × | 97 |
Q10 | 725 | × | 101 |
Long division
Long division calculations, like long multiplication calculations, can be completed quickly and easily without a calculator if you know the multiplication tables well. There are four steps in a long division calculation, and as long as you follow these in order, you will arrive at the right answer.
Worked example
Q: Divide 156 by 12
This may seem obvious, but recognize which number you are dividing
into
. This is called the
dividend
. In this case you are dividing the dividend (156) by the
divisor
(12). Be clear about which is the divisor and which is the dividend – this will become very important when you divide very large or very small numbers.
There are four steps in a long division question.
Step 1 Divide (
D
)
Step 2 Multiply (
M
)
Step 3 Subtract (
S
)
Step 4 Bring down (
B
)
You can remember this as D-M-S-B with any mnemonic that helps you to remember the order.
D
o-
M
ind-
S
lippery-
B
ananas.
D
irty-
M
uddy-
S
alty-
B
icycles. Follow the steps in order and repeat until you have worked through the whole calculation.
Step 1: Divide
Work from the left to the right of the whole number. 12 divides into 15 once, so write ‘1’ on top of the division bar.
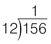
Step 2: Multiply
Multiply the result of Step 1 (1) by the divisor (12):
1 × 12 = 12. Write the number 12 directly under the dividend (156).
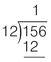
Step 3: Subtract
Subtract 12 from 15 and write the result directly under the result of Step 2.
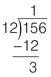
Step 4: Bring down
Bring down the next digit of the dividend (6).
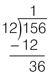
Return to Step 1 and start the four-step process again.
Step 1
:
D
ivide 12 into 36 and write the result (3) on top of the long division sign.
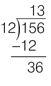
Step 2
:
M
ultiply the result of Step 1 (3) by the divisor (12): 3 × 12 = 36. Write the number 36 directly below the new dividend (36).
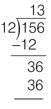
Step 3
:
S
ubtract 36 from 36.
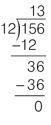
Step 4
: There aren’t any more digits to
B
ring down, so the calculation is complete.
156 ÷ 12 = 13
You will learn about long division with remainders and decimals in
Chapter 2
.
Long division: practice drill 1
Set a stopwatch and aim to complete these calculations in four minutes. You may check your answers with a calculator only once you have finished all the questions in the drill.